|
|
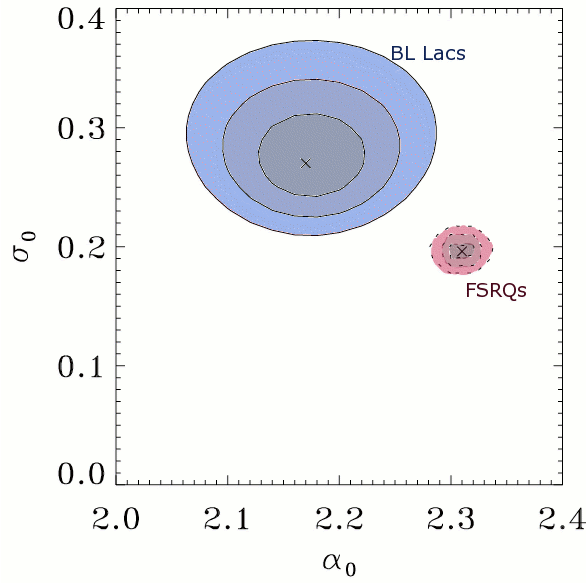
Spectral Indices of Blazars:
|
|
However, the spectral index distribution is not easy to measure. With only a handful of photons mesured from each blazar, determination of individual spectral indices involves large measurement errors, which can appreciably affect how well we reconstruct the underlying distribution. Whatsmore, blazars flare frequently, and during these flares their emission spectrum may change. In this paper, we employ a likelihood approach to unveil the intrinsic distribution of spectral indices of gamma-ray loud blazars detected by EGRET, and show how the same technique cna be applied to GLAST data to confidently constrain the distribution parameters and how these may change among blazar classes and flaring states. Reference: Venters, T.M. & Pavlidou, V. 2007, ApJ, 666, 128 |
|