|
|

|
Astronomical Media
The following is a collection of media pertaining astronomical data obtained with the Palomar telescopes. Please see conditions of use. For use of media not exclusively credited to Palomar Observatory, please contact its original source.
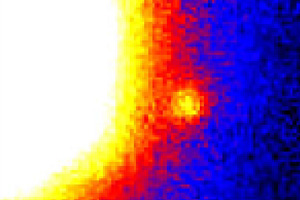
Brown dwarf Gl 229B, 60-inch telescope, 1994. (Caltech/JHU/NASA)
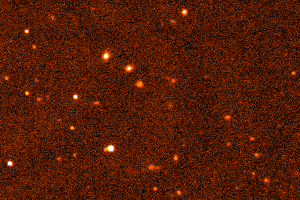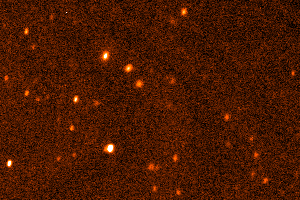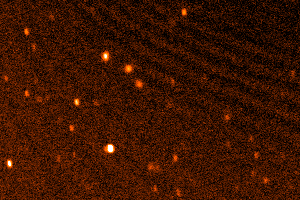
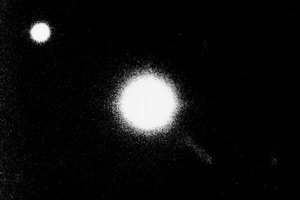
Dwarf planet Eris, Samuel Oschin Telescope, 2003. (Palomar/Caltech/M.Brown)
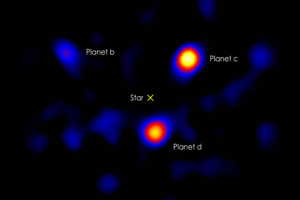
Exoplanets in HR8799 by the Hale Telescope, 2010. (NASA/Caltech/Palomar)

The Crab Nebula pulsar as imaged by CHIMERA, 2014. (Palomar/Caltech/CHIMERA)

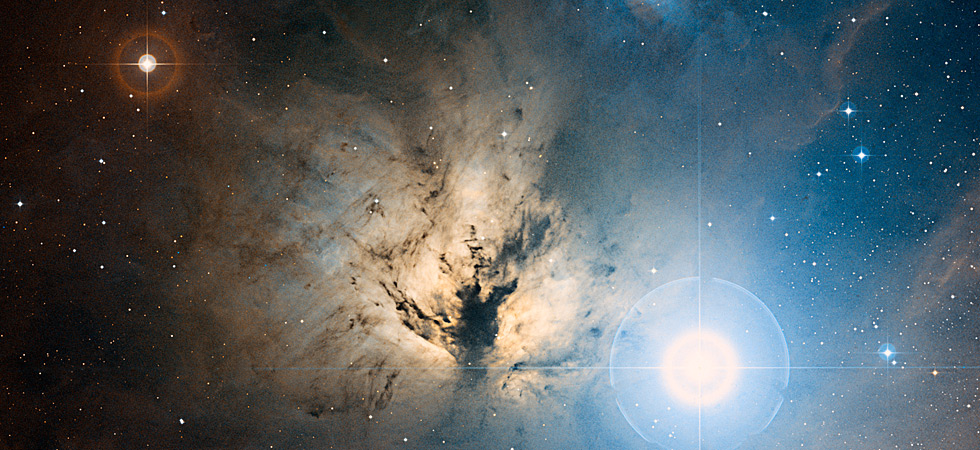
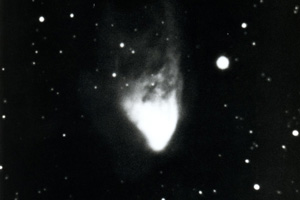
The Flame, Horsehead, and Orion nebulas by ZTF, 2017. (Palomar/Caltech/ZTF)

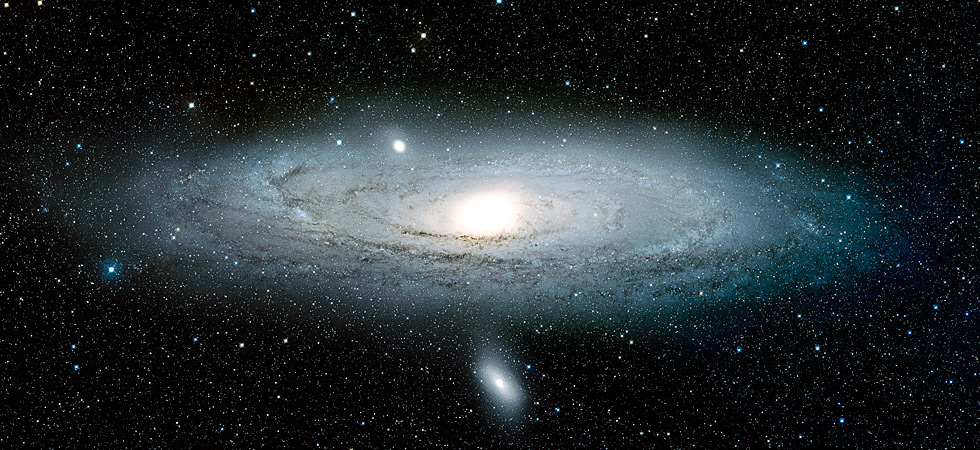
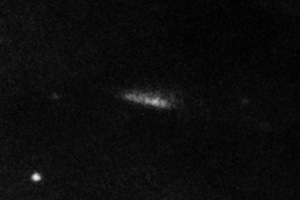
The Andromeda Galaxy as imaged by ZTF, 2019. (Palomar/Caltech/ZTF)
The First Deep-Sky Images in “Natural” Color
Our digital exhibit The Universe in Color explores the novel methods developed by astrophotographer William C. Miller in the late 1950s to capture the distant universe in full color with the Hale and Samuel Oschin telescopes.
The Universe in Color: the first "natural color" deep-sky photographs slideshow, 26 images. Click ► to start. Use < or > to reverse or advance one slide, or the progress dots to jump slides. Click any image to enlarge and on some captions for further context.
Images from the Second Palomar Observatory Sky Survey (POSS II)
The Second Palomar Observatory Sky Survey (POSS II) by the 48-inch Samuel Oschin Telescope produced some of the most iconic astronomical images of all time. The POSS II plates were digitized as part of the STSci Digital Sky Survey (DSS) and are available online to anyone from the DSS site. Enthusiasts have reprocessed the images using modern techniques to produce spectacular digital views of deep sky objects.
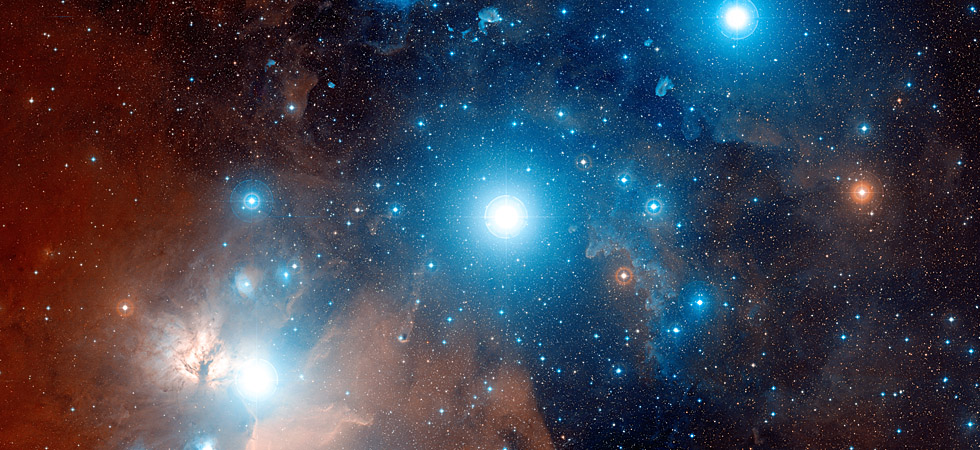

The Horsehead Nebula (IC 434), the Flame Nebula (NGC 2024), and Orion's Belt. (Palomar/Caltech/DSS/D.De Martin)
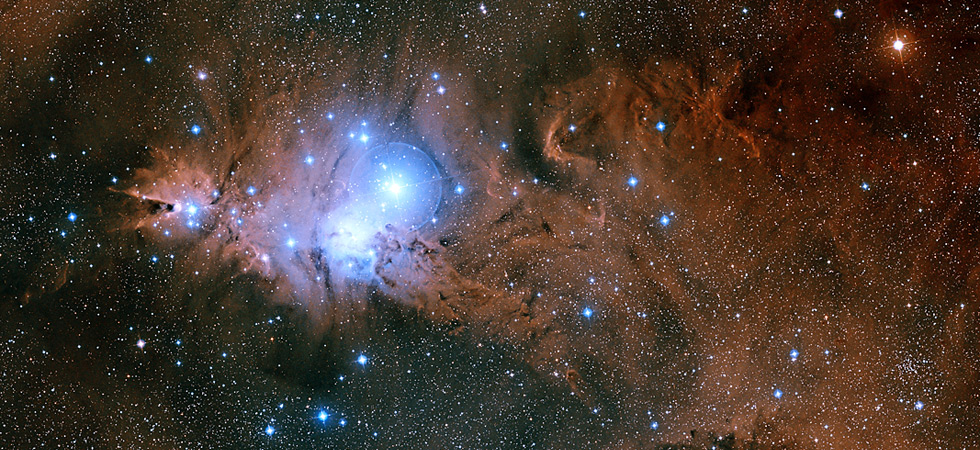

The Christmas Tree Cluster, the Cone Nebula, and Fox Fur Nebula (NGC 2264) in the constellation Monoceros. (Palomar/Caltech/DSS/D.De Martin)
Scientific Legacy
A collection of short videos that summarize highlights of observatory scientific achievements.
Measuring Cosmic Distances (2020)
Palomar Observatory's role in measuring distances and determining the size of the Universe. Duration: 3:33 min. (Palomar/Caltech)
Cosmic Chemistry (2020)
How Palomar contributed to our understanding of stellar nucleosynthesis. Duration: 2:38 min. (Palomar/Caltech)
Mapping the Palomar Sky (2024)
The Palomar Schmidt telescopes as pioneering and prolific sky reconnaissance instruments. Duration: 6:20 min. (Palomar/Caltech)
The New Solar System (2020)
About Palomar Observatory's role in providing a fuller understanding of our Solar System's architecture. Duration: 3:32 min. (Palomar/Caltech)
The Hearts of Galaxies (2020)
One of Palomar's greatest scientific hits led to the fascinating discovery of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. Duration: 3:33 min. (Palomar/Caltech)
Questions? We've answered many common visiting, media, and academic questions in our public FAQ page.
Please share your feedback on this page at the
COO Feedback portal.
Astro Media / v 1.0.6
Last updated: 14 March 2024 ACM
|
|
|